Bad loan problem is one of the biggest challenges for a nation. A debt pile impacts the valuations of companies and their overall financial health. This in turn is a reason behind the slowing down of the economic growth of a country. When the bad debts reach a certain level, financial institutions are also unwilling to lend in such circumstances, thereby, increasing the problem of non-availability of credit. Policymakers in different countries understand the importance of getting out of this situation and have taken several steps in the right direction, but success has not yet been forthcoming.
Let us now understand what one means by deleveraging of debts?
The process by which a financial institution reduces their level of indebtedness, by increasing their capital and reducing assets is called deleveraging of debts. In other words, deleveraging is the reduction of debt and the most direct way for an entity to deleverage is to immediately pay off any existing debts and obligations on its balance sheet.
The Asian market for distressed loan is young and fragmented but has huge potential, specially after the Covid-19 pandemic. Distressed assets are assets which are unable to service interest and principal for more than 180 days and subsequently become delinquent. They are inversely proportional to economic growth as these assets only end up consuming additional capital.
A company can use the following techniques to deleverage:
- Deleverage by selling assets, bonds, and a part of the business at a discount (Debt Sale)
- Refinance existing debt to reduce monthly payments and interest rates
- Deleverage by using excess cash from operational activities
- Deleverage by issuing more share on the stock market
Debt Sale:
When banks and financial institutions (FIs) sell their portfolios to a third party or collection agencies, it is called debt sales. The sale of debt by lenders/ creditors to buyers is generally done at a discounted rate. When a debt buying company purchases an account from a creditor, it purchases the contracts and all rights, benefits and liabilities that were held by the creditor associated with the contract. These purchases can include accounts that are performing (i.e., making payments), as well as those that are nonperforming (in default). However, most of the time debt sales is mostly performed on stressed portfolios which are mostly deemed unrecoverable.
Debt sales is generally resorted by lenders for the following reasons:
- Strategic sales to rebalance their exposures either in sectors or in certain large conglomerates or
- Reducing overall book size by selling the complete portfolio to free up capital or
- To achieve resolution of stressed assets by extinguishing the exposures.
Developing strategies for management of NPLs
Financial institutions need to address their NPL problems by developing a detailed strategy for its supervision. This includes the following steps:
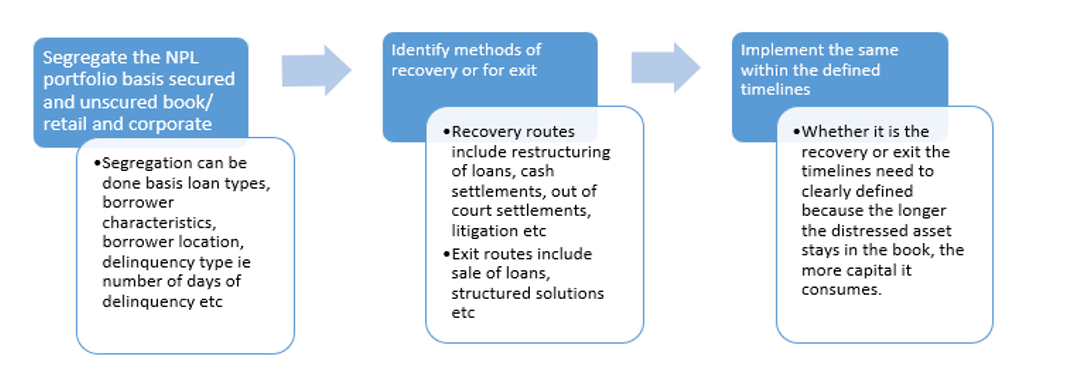
Collection strategy of NPL accounts begins with portfolio classification and bucket categorisation sorted as performing loans DPD 0-30, 30-60, 60-90, DPD 90-360 days and DPD>360 days. Once the portfolio has been clearly identified and bucketed, creditors need to decide upon which portfolio to be collected internally, which to be outsourced and which to be sold. The following table can be followed to recognise the same:
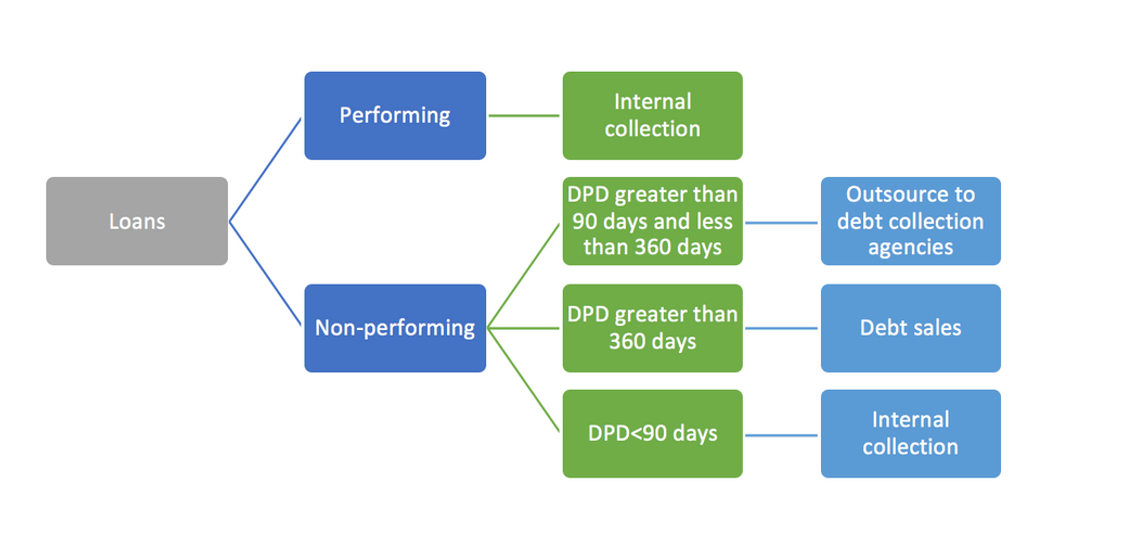
Portfolio Selection Criteria
Financial institutions need to identify the portfolio which needs to be sold. Thus, a criteria dependent on following factors can be developed:
- Collection strategy– This is basically when the third party decides which bucket of loans does it want to buy, it can depend on the amount, the number of days, the commission factor, etc.
- Portfolio Pricing – How and what is the right and fair pricing for each portfolio. How will that pricing be determined? Due to the greater difficulty of evaluating the price of unsecured portfolio, by partnering with third parties in a transparent fashion, there are many options of portfolio sale, some including receiving a fixed price with some potential upside if recoveries are beyond a certain level.
- Bank’s internal strategy and risk appetite – Depends on the staff strength, their expertise, and stakeholders’ preferences.
- Operational and cost challenges – Cost benefit analysis to determine which is better- selling or owning (self-collecting) the portfolio and type of portfolio to be sold
- Market demand / investor’s interest – Is the market available for the decided sale?
Conclusion:
Deleveraging of debts helps the company to get rid of toxic debt, a type of debt where the company cannot pay back the interest and principal amount. A reduction in toxic debt will reduce the number of liabilities on the balance sheet and improve financial ratios, which will be looked at favorably by lenders and investors. Thus, policymakers should work towards taking steps to have more inclined methods and processes for deleveraging of debts, thereby helping the credit ecosystem.


 International (EN)
International (EN) India (EN)
India (EN)


